
Akut apandisit 1309 (%63,1), gangrenöz-perfore apandisit 305 (%14,7), negatif apendektomi 105 (%5,1), flegmanöz apandisit 32 (%1,5), beklenmeyen patolojik bulgular ise 62 (%3) hastada saptandı. Bu hastalar 1368 (%66) erkek olup, toplam yaş ortalaması 33☑2,9 idi. Bulgular: Toplam 2076 hasta çalışmaya dahil edilip analiz edildi. İstatistiksel analizde Fisher’s ki-kare testi kullanıldı. Patoloji sonuçları genel bulgular ve beklenmeyen bulgular olarak iki kategori altında incelendi. Patoloji preparatları iki patolog tarafından tekrar değerlendirildi. Hastaların cinsiyet, yaş ve patoloji sonuçları analiz edildi. İnsidental apendektomiler çalışma dışı bırakıldı. Ersin Arslan Eğitim ve Araştırma Hastanesi’nde Ocak 2016-Şubat 2020 tarihleri arasında akut apandisit tanısıyla acil opere edilen hastalar retrospektif olarak tarandı. Biz burada hastanemizde akut apandisit tanısıyla opere edilen 2076 hastanın patoloji sonuçlarını ve bunlar arasında beklenmeyen histopatolojik bulguları literatür eşliğinde sunmayı amaçladık. Ancak bazı nadir durumlar da lümen obstrüksiyonu yaparak akut apandisite neden olabilmektedir. Fekaloit ve lenfoid hiperplazi lümen obstrüksiyonuna neden olan en yaygın nedenlerdir. Apandisitin etiyolojisi hala tam olarak bilinmemekle birlikte olası nedenler arasında lümen obstrüksiyonu yer alır. Öz:Amaç: Akut apandisit dünya üzerinde en sık acil karın ameliyatıdır. Among the unexpected pathological findings were fibrous obliteration in 31 (50%) patients, mucosal hyperplasia in 8 (13%) patients,appendicular diverticulitis in 7 (11.3%) patients, retention cyst in 5 (8.1%) patients, mucinous cystadenoma in 3 (4.8%) patients, well-differentiatedneuroendocrine tumor in 2 (3.2%) patients, eosinophilic infiltration in 2 (3.2%) patients, foreign body reaction in 2 (3.2%) patients, granulomatousappendicitis in 1 (1.6%) patient, and parasitic infestation was detected in 1 (1.6%) patient.Conclusion: Unexpected histopathological findings are rare in appendectomy specimens and these diagnoses help guide the patient’s treatment. Acute appendicitis was found in 1309 (63.1%) patients, gangrenous-perforated appendicitis in 305 (14.7%) patients,negative appendectomy in 105 (5.1%) patients, phlegmonous appendicitis in 32 (1.5%) patients, and unexpected pathological findings in 62 (3%)patients. Of the patients, 1368 (66%) were man, 708 (34%) were woman, and themean age was 33☑2.9 years. Fisher’s chi-square test was used for statistical analysis.Results: A total of 2076 patients were included in the study and analyzed. Pathology results wereanalyzed under two categories as general findings and unexpected findings. Pathology preparations were reassessed by two pathologists. Data of 2076 patients were reached.Gender, age, and pathology results of the patients were analyzed. ErsinArslan Training and Research Hospital were retrospectively screened. Here, we aimed to present the pathology results of 2076patients operated due to acute appendicitis in our hospital and the unexpected histopathological findings in the light of the literature.Method: Patients who were emergently operated with diagnosis of appendicitis between January 2016 and February 2020 in Gaziantep Dr. Fecaloid and lymphoid hyperplasia are the most common causes of lumen obstruction.However, some rare conditions may cause acute appendicitis by causing lumen obstruction. Although the etiology of appendicitis is still notfully known, possible causes include lumen obstruction. The question of duration of screening in a young patient with no significant family history is difficult to answer.Abstract: Aim: Acute appendicitis is the most common cause of emergency abdominal surgery in the world. Given the rarity of the condition, we suggest routine follow-up of all patients by clinical and serological screening for systemic vasculitis.

Careful histological examination is required to identify vasculitis. Polyarteritis nodosa is the most commonly associated systemic vasculitic disease. A risk of systemic vasculitis approaching 30% has been reported in some studies, 1 however these are limited by study size.
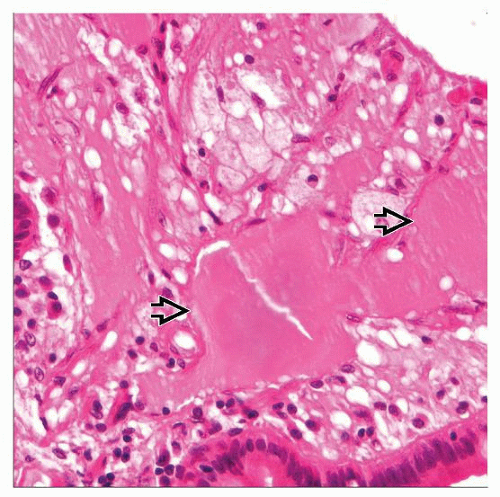
Our patient showed no clinical signs of vasculitis and tested negative for pANCA, cANCA, ANA and ENA. Isolated necrotising vasculitis of the appendix is an uncommon finding of long debated relatedness to systemic vasculitic disorders.

Histological examination showed fibrous obliteration of the tip with necrotising vasculitis involving small to medium-sized arteries comprised of fibrinoid necrosis and neutrophilic infiltrate, karyorrhexis and cuffing by histiocytes and lymphocytes. Here we repo rt a case of necrotising arteritis of the appendix in a 17-year-old male presenting with right lower quadrant pain.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
